About
MJS Commodities is a leading privately held international trading company and a subsidiary of MJS Global Group.
Our team has 200+ years combined experience in the procurement and delivery of commodity products and services.
We specialize in the handling of every element involved in the international trade of physical commodities with the focus on high-quality agro products, precious metals, polished diamonds and gemstones, solid and liquid fuels, and hydrocarbon-free 100% biodegradable packaging we move soft and hard commodities from remote locations to where they are most needed – reliably, professionally and efficiently.
We operate, market and advice on multiple raw materials to various client segments around the globe, whether they are import-export businesses, financial institutions, governments and private investors, through the supply chain and bringing them wherever needed.
Our thoughtful services, diversified product lines, and relationships are advanced with integrity and honest straightforward dealing and go to great lengths to ensure professionalism, excellence, and peace of mind. Whether you’re a producer, an existing or potential partner in government or business, or an end-user we have the focus, passion, and commitment to get you closer to your markets.
We value the success and accomplishments of our principals as we value our company and people. By combining both of our visions, the results are limitless. Our attitude is making all possible efforts, instead of deeming it impossible, with a conviction to take the business deal to successful completion to enrich both our clients and our societies.
World Trade and Market Protection Terms
Glossary of Trade and Market Protection Related Terms.
A
ACCESSION
A government joining the WTO. As part of the accession to the WTO pursuant to Article XII, the acceding government negotiates concessions and commitments relating to Market Access for Goods and Services with WTO Members.
ACPs
Countries in Africa, the Caribbean and the Pacific which benefit from a preferential tariff treatment in the E.C., under the Lomé Convention.
Accounting rate
In telecoms, the charge made by one country’s telephone network operator for calls originating in another country.
Administered Protection
See Contingent Protection.
Ad Valorem
An ad valorem duty (tariff, charge, and so on) is based on the value of the dutiable item and expressed in percentage terms for example, a duty of 20 percent on the value of automobiles.
Ad Valorem Equivalent (AVE)
An ad valorem equivalent is the equivalent in percentage of a specific duty, mixed, compound or other duty containing a specific element. An ad valorem equivalent is calculated for each customs duty that is not ad valorem. The AVE is calculated from the actual duty collection or from the unit value of imports. For example, the AVE of a specific duty of $1.00 per KG levied on a product with a unit value of $10.00 per KG is equal to 10% ($1.00/$10.00).
Agenda 21
The Agenda for the 21st Century – a declaration from the 1992 Earth Summit (UN Conference on the Environment and Development) held in Rio de Janeiro.
Aggregate
See Product Aggregate
AGOA (African Growth and Opportunities Act)
U.S. legislation providing duty-free access for a large number of products for 35 African economies.
All Partners
Shortcut used in WITS to select all trade partners. When “All Partners? is selected, WITS returns one row of information for each and every partner.
Anti-dumping duties
Article VI of the GATT 1994 permits the imposition of anti-dumping duties against dumped goods, equal to the difference between their export price and their normal value, if dumping causes injury to producers of competing products in the importing country.
APEC
Asian Pacific Economic Cooperation forum.
Appellate Body
An independent seven-person body that, upon request by one or more parties to the dispute, reviews findings in panel reports.
Appellations of origin
Indications of where goods originate with characteristic qualities which are due exclusively or essentially to the geographical environment (for example, “Bordeaux” of “Roquefort”).
Armington Preferences
Goods are differentiated (imperfect substitutes) by exporting country. This assumption is used in the SMART model included in WITS in order to avoid a big bang solution.
Article XX
GATT Article listing allowed “exceptions” to the trade rules.
ASEAN
Association of Southeast Asian Nations. The six ASEAN members of the WTO – Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand – usually speak in the WTO as one group on general issues.
ATC
The WTO Agreement on Textiles and Clothing which integrates trade in this sector back to GATT rules within a ten-year period.
Automaticity
The “automatic” chronological progression for settling trade disputes in regard to panel establishment, terms of reference, composition and adoption procedures.
Autonomous Duty
See Statutory Duty
Average (Tariff)
A tariff average measures the average level of nominal tariff protection. There are two types of tariff averages: a simple average and a trade-weighted average. The example below illustrates how those two types of tariff averages are calculated.
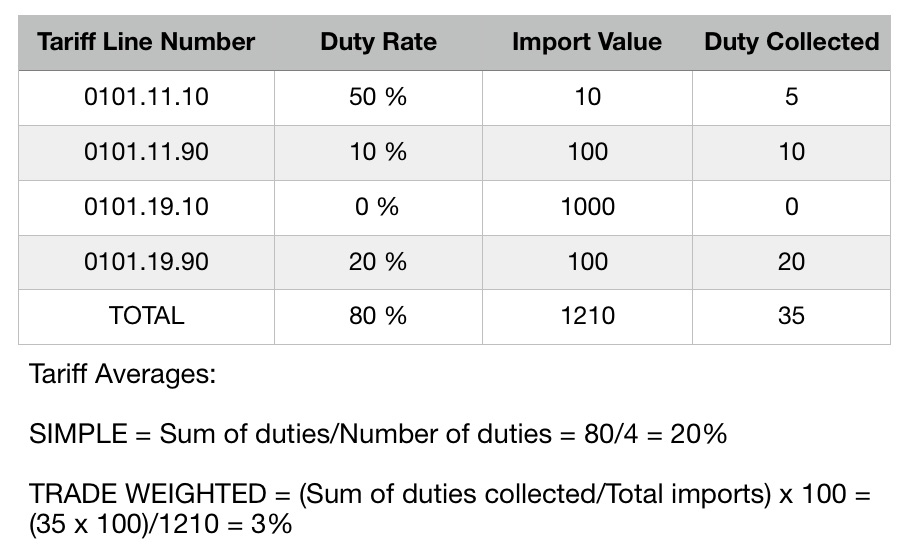
It should be noted that the trade-weighted average is often lower than the arithmetic average. This is because theoretically, low duties carry more imports than high duties. Subsequently, in the trade-weighted average, low duties are given more weight than high duties, thus introducing a downward bias. In the arithmetic average, each duty carries the same weight, whatever its level.
B
Backward Conversion
Consists of converting information from a given nomenclature to an older one. Backward conversion is generally safer (than upward conversion) since the destination nomenclature is made of fewer lines. The conversion mostly consists of line aggregation and reduction of the product structure.
Basel Convention
An MEA dealing with hazardous waste.
Berne Convention
Treaty, administered by WIPO, for the protection of the rights of authors in their literary and artistic works.
Binding
See Tariff Binding.
Binding Coverage
Statistical measure defined as the number of bound lines divided by the total number of tariff lines.
Binding Overhang
Often used to describe a situation where there is a large difference between the tariff that is actually applied (MFN Applied) and the level at which the tariff is bound in GATT (the ‘ceiling’).
Border protection
Encompasses any measure which acts to restrain imports at point of entry.
Border Tax Adjustment
Fiscal measure compensating, in whole or in part, for the different treatment either between imports and similar domestic products or between exports and similar products sold on the domestic market. For example, refunds of domestic indirect taxes on goods destined for export; or changes on imports similar to the taxes levied on like domestic products. Also see Duty Drawback.
Bound
See Tariff Binding
Breakdown
Used in WITS when a region (group of countries) is used to produce individual information for each and every country belonging to that region.
BTA
Border tax adjustment.
C
Cabotage
In maritime transport, sea shipping between ports of the same country, usually along coasts.
Cairns Group
Coalition of developing and industrialized country exporters of agricultural commodities formed in the Uruguay Round to negotiate stronger multilateral disciplines on agricultural trade policies.
CAP
Common Agricultural Policy – comprehensive system of production targets and marketing mechanisms designed to manage agricultural trade within the EC and with the rest of the world.
Carry Forward
When an exporting country uses part of the following year’s quota during the current year.
Carry Over
When an exporting country utilizes the previous year’s unutilized quota.
Category (Product)
Product categories are defined on an ad hoc basis to compile summary reports by sectors, stages of processing, etc. Product categories are generally defined in terms of four-digit headings of the CCCN or in terms of six-digit groups of the HS.
Ceiling binding
A binding is “ceiling” if the applied duty is lower than the bound duty. The following example illustrates the difference between “ceiling” bindings and bindings at “prevailing” level. See also Binding overhang.
Chapter
The CCCN and the HS are structured nomenclatures. The first two digits of CCCN and HS numbers represent the chapter level. The CCCN comprises 99 chapters and the HS 97 chapters. HS chapter 77 is not used at present.
CIF
See Cost, Insurance and Freight.
Circumvention
Measures taken by exporters to evade anti-dumping or countervailing duties.
CITES
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species. An MEA.
Clusters
In WITS, refers to all product categories for a given level of details (or Tier). Cluster selection is used in WITS in order to select many same level product categories in one click.
Commercial
Having an office, branch, or subsidiary in a foreign country.
Conferences
In maritime transport, groups of container lines which have anti-trust immunity for the purpose of collectively setting rates.
Contracting Parties
Refers to the nations which signed the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade. When the term is capitalized, it means all Contracting Parties acting jointly.
Cost, Insurance and Freight (CIF)
The cost of a good delivered to the importing country’s port.
Counterfeit
Unauthorized representation of a registered trademark carried on goods similar to goods for which the trademark is registered, with a view to deceiving the purchaser into believing that he/she is buying the original goods.
Countervailing
Action taken by the importing country, usually in the form of increased duties, measures to offset subsidies given to producers or exporters in the exporting country.
Chapter
First level sub-category (2-digit) used in the Harmonized System (HS) nomenclature.
Classification
See Nomenclature.
Commercial presence
The possibility of a service provider to be physically present (a branch or subsidiary, for instance) in the “importing” market.
Common External Tariff
A uniform tariff adopted by a customs union (e.g. the European Communities) to be assessed on imports entering a region from countries outside the union.
Compound Duty
A compound duty is a tariff duty comprising an ad valorem duty to which is added or subtracted a specific duty: 10% plus $2.00/KG; 20% less $2.00/KG.
Computable general equilibrium (CGE) models
Mathematical characterizations of the economy, used to predict the impact of policy changes taking into account both direct effects as well as indirect effects that work through labor and other markets.
UN COMTRADE
See UNSD Commodity Trade Statistics Database
Concession
A tariff reduction, tariff binding or other agreement to reduce import restrictions: usually accorded pursuant to negotiation in return for concessions by other parties.
Concordance
Table relating two different nomenclatures, item by item.
Consumer Welfare
It is the “enjoyment’ that consumers are inferred to gain from their consumption. While welfare cannot be measured directly, economists often use a measure of real income or purchasing power as a way of measuring welfare in money terms. The SMART model (included in WITS) does not directly estimate consumer welfare, but the welfare change includes the change in consumer surplus following a tariff reduction.
Content, Domestic or Local
Rules establishing a minimum proportion (by value or volume) of a product that has must be domestically or locally produced in order to obtain a benefit (e.g., a tariff concession or permission to be offered for sale).
Contingent Protection
Trade barriers that are imposed if certain circumstances (contingencies) are met. Examples include anti-dumping or countervailing duties (to offset subsidies) and safeguards. Also called Administered Protection.
Cotonou Agreement
Partnership agreement between the EU and the ACP countries signed in June 2000 in Cotonou, Benin. Replaces the Lomé Convention. Its main objective is poverty reduction, “to be achieved through political dialogue, development aid and closer economic and trade cooperation.”
Countervailing Duty
Duty levied on imports of goods that have benefited from production or export subsidies. The duty is intended to offset the effect of the subsidy.
CTD
The WTO Committee on Trade and Development.
CTE
The WTO Committee on Trade and Environment.
CTG
Council for Trade in Goods – oversees WTO agreements on goods, including the ATC.
Current Bound
Current value of the bound tariff for a given year. Concessions offered in GATT negotiations are sometimes staged over a period of several years before the concession is fully implemented. Until then, there may be a current bound (used as ceiling for the current MFN Applied tariff) higher than the final Bound (final commitment).
Customs Duty
Charge levied on imports and listed in importing country’s tariff schedules. Duties may be specific or ad valorem or a combination of the two (ad valorem with a specific minimum, or the greater of the two).
Customs Union
A group of countries forming a single customs territory in which (1) tariffs and other barriers are eliminated on substantially all the trade between the constituent countries for products originating in these countries, and (2) there is a common external trade policy (common external tariff) that applies to nonmembers.
Customs Valuation
Establishment, according to defined criteria, of the value of goods for the purpose of levying ad valorem customs duties on their importation.
D
Data Source
Refers in WITS to the database used to retrieve information.
Deep integration
Inter-governmental cooperation in designing and applying domestic policies such as taxes, health and safety regulations, and environmental standards. May involve either harmonization of policies or mutual recognition; generally occurs in the context of regional integration agreements.
Deficiency payment
Paid by governments to producers of certain commodities and based on the difference between a target price and the domestic market price or loan rate, whichever is the less.
Degressivity
Mechanism to ensure that the application of a measure gradually becomes less severe over time. For example, a tariff set at 50 percent that is reduced by 10 percentage points each year and becomes zero in year 5.
Derived Nomenclature
Alternative nomenclature used to display information via a concordance table between the native and the derived nomenclature.
Differential and more favorable treatment
See Special and Differential Treatment and Enabling Clause.
Dispersion (Tariff)
The tariff dispersion is generally analyzed by compiling tariff profiles. Tariff profiles show a distribution of tariff lines according to duty ranges as follows:
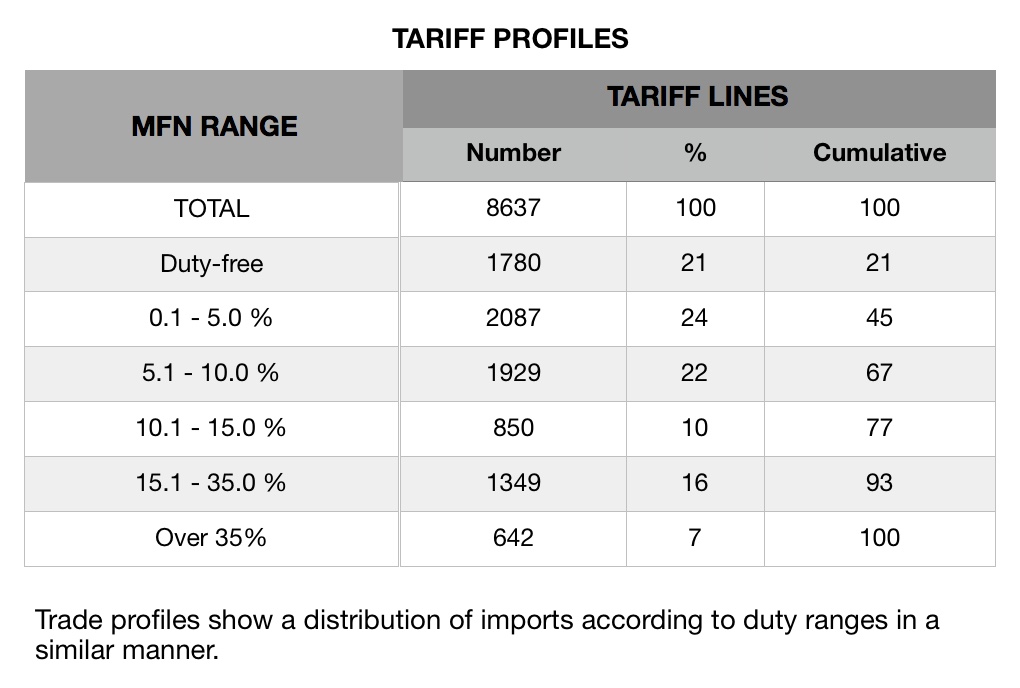
Division
Second level sub-category (2-digit) used in the SITC nomenclature.
Doha Round
Current (9th) round of WTO negotiations.
Domestic Content
See Content.
DSB
Dispute Settlement Body – when the WTO General Council meets to settle trade disputes.
DSU
The Uruguay Round Understanding on Rules and Procedures Governing the Settlement of Disputes.
Dumping
A form of price discrimination by which the export price of the product exported from one country to another is less than the comparable price, in the ordinary course of trade—that is, including transport and related costs—for the like product when destined for consumption in the exporting country (GATT Art. VI). Also defined as sales below the estimated cost of production. The margin of dumping is the difference between the two prices.
Duty-drawback Scheme
A duty drawback scheme (often administratively demanding) is a form of Border Tax Adjustment whereby the duties or taxes levied on imported goods are refunded, in whole or in part, when the goods are re-exported. The idea is to reduce the burden on exporters while maintaining tariffs for revenue or protective purposes.
E
EBA
See Everything But Arms.
EC
European Communities.
EEP
Export enhancement programme – programme of US export subsidies given generally to compete with subsidized agricultural exports from the EC on certain export markets.
Effective Rate of Protection
A measure of the protection afforded by an import restriction calculated as a percentage of the value added in the product concerned. Takes into account the protection on output and the cost raising effects of protection on inputs.
Effectively Applied Duty
A customs duty which is lower than the statutory duty. The effectively applied duty can be for an undetermined period of time or for a limited period of time (temporary duty). Effectively applied duties are sometimes passed by Parliament or decided on and put into effect by a government for economic reasons.
EFTA
European Free Trade Association.
Emergency Action
See Safeguard Action.
Enabling Clause
1971 GATT Decision on “Differential and More Favorable Treatment, Reciprocity and Fuller Participation of Developing Countries”. One of the so-called Framework agreements, it enables WTO members, notwithstanding the nondiscrimination requirements, to “accord differential and more favorable treatment to developing countries, without according such treatment to other contracting parties.” See also Generalized System of Preferences.
Escalation (Tariff)
See Tariff Escalation.
Escape Clause
Clause in a legal text allowing temporary derogation from its provisions under certain specified emergency conditions. See also Safeguard Action (GATT Art. XIX.)
EST
Environmentally-sound technology.
EST&P
EST and products.
Ex ante, ex post
Before and after a measure is applied.
Everything But Arms
A 2001 EU initiative to grant least developed countries duty- and quota-free access for their exports.
Excise Duty
Also known as fiscal tax or revenue duty. See Fiscal Tax.
Export-performance
Requirement that a certain quantity of production must be exported.
Export Processing Zone (EPZ)
A designated area or region in which firms can import duty-free as long as the imports are used as inputs into the production of exports. Traditional EPZs are fenced-in industrial estates specializing in manufacturing for exports. Modern ones have flexible rules that may permit domestic sales upon payment of duties when leaving the zone. EPZs generally also provide a liberal regulatory environment for the firms involved as well as infrastructure services.
F
Final Bound
The value of the Bound tariff at the end of the implementation period. Concessions offered in GATT negotiations are sometimes staged over a period of several years before the concession is fully implemented. Until then, there may be a current bound (used as ceiling for the current MFN Applied tariff) higher than the final Bound (final commitment).
Finished Products
The third stage of processing in the measurement of tariff escalation. Finished products are processed products which can be sold to consumers without further processing.
Fiscal Tax
A tax which is levied on imported products as well as on domestically produced goods to generate revenue. A fiscal tax is therefore not equivalent to a customs tariff duty since it has no protective effects. Fiscal taxes are sometimes included in the customs tariff duties. In such cases, the fiscal element of the duty is deducted from the tariff duty. Only the protective part of the duty is recorded in the IDB tariff files.
FOB
See Free On Board.
Food security
Concept which discourages opening the domestic market to foreign agricultural products on the principle that a country must be as self-sufficient as possible for its basic dietary needs.
Foreign Trade Zone
An area within a country where imported goods can be stored or processed without being subject to import duty. Also called a “free zone,” “free port,” or “bonded warehouse.” See also Export Processing Zone.
Formula Approach
Method of negotiating down tariffs or other barriers to trade by applying a general rule (formula). For example, a rule specifying that all tariffs are to be cut to a certain fraction of their initial level, or that an agreement should cover a certain proportion of economic activity (sectors).
Free on board (FOB)
The price of a traded good including its value and the costs associated with loading it on a ship or aircraft, but excluding international transportation (freight) costs, insurance and payments for other services involved in moving the good to the point of final consumption.
Free-rider
A casual term used to infer that a country which does not make any trade concessions but profits, nonetheless tariff cuts and concessions made by other countries negotiating under the most-favoured nation principle.
Free-Trade Area
A group of countries in which the tariffs and other barriers are eliminated on substantially all trade between them. Each member maintains its own external trade policy against nonmembers. Also called free trade agreement or free trade arrangement. Contrasts with Custom Union.
G
G7
A group of seven major industrialized countries whose heads of state have met annually since 1976 in summit meetings to discuss economic and political issues. The seven are United States, Canada, Japan, Britain, France, Germany, and Italy.
G-8
The G7 plus Russia, which have met as a full economic and political summit since 1998.
G15
Group of 15 developing countries acting as the main political organ for the Non-Aligned Movement.
G-20
International forum of finance ministers and central bank governors representing 19 countries plus the EU. Created in 1999 by the G-7 with the aim to promote discussion, study and review of policy issues among industrialized and emerging market countries to promote international financial stability. The Managing Director of the IMF, the President of the World Bank, and the Chairpersons of the International Monetary and Financial Committee and Development Committee of the IMF and World Bank participate in G-20 deliberations.
G-21
A block of developing countries led by Brazil, China and India that emerged just before the Cancun meeting. It represents half the world’s population and two-thirds of its farmers.
G-24
Established in 1971, an inter-governmental group of 24 developing countries that has the objective to concert the position of the developing countries on monetary and development finance issues. The only formal developing country grouping within the IMF and World Bank. Meets twice a year, preceding the Spring and Fall meetings of the two institutions.
G-77
A coalition of developing countries within the United Nations, established in 1964 at the end of the first session of UNCTAD, intended to articulate and promote the collective economic interests of its members and enhance their negotiating capacity. Originally with 77 members, it now (in 2002) has 133.
GATS
General Agreement on Trade in Services.
GATT
General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade, which has been superseded by the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
GATT 1947
Refers to the old version of the GATT.
GATT 1994
The new version of the General Agreement, incorporated into the WTO, which governs trade in goods.
General obligations
Obligations which should be applied to all services sector at the entry into force of the agreement.
General Tariff
General tariffs are the customs duties which apply in some countries to partners which are not members of the WTO. The general duties are generally higher than the MFN duties.
Generalized System of Preferences (GSP)
The GSP is a system through which industrialized high-income countries grant preferential access to their markets to developing countries. Also called Generalized System of Trade Preferences.
Global Simulation
Extension of the SMART model to simulate the partial equilibrium impact of tariff reductions in a multi-market framework.
Graduation
Concept linking the rights and obligations of a developing country to its level of development. Referred to in WTO Trade Policy Review Mechanism. Generally used in the context of GSP and similar types of preferential treatment of low income countries as a mechanism or set of criteria to determine when countries cease to be eligible for preferences.
Group
Third level sub-category (3-digit) used in the SITC nomenclature.
GRULA
Informal group of Latin-American members of the WTO.
GSP
See Generalized System of Preferences.
GTAP
The Global Trade Analysis Project, based at PurdueUniversity in the United States. It provides data and models for computable general equilibrium modeling. See Computable general equilibrium
GSIM
See Global Simulation
H
Harmonized System (HS)
“Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System”. Nomenclature developed by the World Customs Organization for customs tariffs and international trade statistics to organize products through hierarchical categories. It is arranged in six digit codes allowing all participating countries to classify traded goods on a common basis. Beyond the six digit level, countries are free to introduce national distinctions for tariffs and many other purposes.
Heading
Second level sub-category (4-digit) used in the Harmonized System (HS) nomenclature.
Heterogeneous Goods
Goods are imperfect substitutes (Assumption used in SMART).
Homogenous Goods
Goods are perfect substitutes.
HS
See Harmonized System.
I
IDB
See WTO Integrated Database
Implementation Period
See Stages Of Reduction
Import Licensing
A procedure which must be followed by importers before they can import goods.
Initial commitments
Trade liberalizing commitments in services which members are prepared to make early on.
Intra-industry trade
Trade in which a country both exports and imports goods that are classified to be in the same industry.
Integration
The phasing out of MFA restrictions in four stages starting on 1 January 1995 and programme ending on 1 January 2005.
Intellectual property
Ownership of ideas, including literary and artistic works (protected by copyright), inventions (protected by patents), signs for distinguishing goods of an enterprise (protected by trademarks) and other elements of industrial property.
Internal support
Encompasses any measure which acts to maintain producer prices at levels above those prevailing in international trade; direct payments to producers, including deficiency payments, and input and marketing cost reduction measures available only for agricultural production.
IPRs
Intellectual property rights.
ISO
International Organization for Standardization.
ITC
Now operated jointly by the WTO and the UN, the latter acting through UNCTAD. Focal point for technical cooperation on trade promotion of developing countries.
ITCB
International Textiles and Clothing Bureau – Geneva-based group of some twenty developing country exporters of textiles and clothing.
Item
In WITS, refers to a product selection mode in which product categories may be individually selected.
L
Labeling
Requirement, either mandatory or voluntary, to specify whether a product satisfies certain conditions relating to the process by which it was produced.
LDC
See Least Developed Country.
LLDCs
Land-locked Least-developed countries.
Least Developed Country (LDC)
A country that satisfies a number of criteria established by the United Nations that together imply a very low level of economic development. As of 2002 the UN had classified 49 countries in the LDC group. Used in WTO Subsidies Agreement, where LDCs are granted differential treatment. Least developed countries are accorded on some countries’ markets a preferential treatment more favorable than GSP (in general duty-free treatment with no limitations).
Land-locked Least-developed countries (LLDC)
Landlocked developing countries are generally among the poorest of the developing countries, with the weakest growth rates, and are typically heavily dependent on a very limited number of commodities for their export earnings. Moreover, of 31 landlocked developing countries 16 are classified as least developed.
LCA
Life cycle analysis – a method of assessing whether a good or service is environmentally friendly.
Licensing (of imports or exports)
Practice requiring approval to be granted by the relevant government authority, or by a body designated by such authority, as a prior condition to importing or exporting.
▪ Automatic licensing
Where approval is freely granted for example, licensing for keeping statistical records.
▪ Non-automatic licensing
Where approval is not freely granted. This may be used as a restriction itself, or it may be used to administer a quota. The license may be subject to certain conditions being met
for example, a requirement to export; the use to which the imported good is to be put; the purchase of a specified quantity of the domestically produced like product; or the availability on the domestic market of the domestically produced like product.
▪ Discretionary licensing
Non-automatic licensing (see above).
Lisbon Agreement
Treaty, administered by WIPO, for the protection of appellations of origin and their international registration.
Local-content
Requirement that the investor purchase a certain amount of local materials for measure incorporation in the investor’s product.
Local (or domestic) content requirements
See Content.
Lomé Agreement
Agreement was between the EU and the ACP countries on trade concessions (GSP treatment), development aid and general cooperation. Replaced by the Cotonou Agreement in 2000.
M
Madrid Agreement
Treaty, administered by WIPO, for the repression of false or deceptive indications of source on goods.
Margin Of Preference
The difference between the duty paid on an MFN basis and the duty paid under a preferential system.
Market Access
Refers to the conditions under which imports compete with domestically produced substitutes. These are determined by the extent to which foreign goods are confronted with discriminatory taxes and other regulations.
Maximum (Minimum) Price System (for imports) Price(s)
Decreed by the authorities of the importing country and above (below) which price(s) imports may not enter the domestic market. Actual import prices below the decreed minimums trigger a protective action, such as the imposition of additional duties or of a quantitative restriction. Different terms are used in different countries and different sectors: basic import price, minimum import price, reference price, and trigger price.
Markup
In WTO terms sometimes used to indicate the extent to which an applied tariff exceeds the bound rate.
MEA
Multilateral environmental agreement.
MFA
Multifibre Arrangement (1974-94) under which countries whose markets are disrupted by increased imports of textiles and clothing from another country were able to negotiate quota restrictions.
MFN
See Most Favoured Nation.
Mirror Data
Used to build data for a non-reported trade flows based on what is reported by all other countries. For example if bilateral import information is missing for a given country, it can be rebuilt using Export information reported by its bilateral partner.
Mixing Regulation
Describes two kinds of practices:
▪ (1) Regulation specifying the proportion of domestically produced content in products offered for sale on the domestic market;
▪ (2) Regulation specifying, for any imports of a given product, the quantity of a domestically produced like product that must be purchased by the importer.
Modes of delivery
Ways in which services may be rendered. They may include sales through establishment, cross-border sales, and the movement of persons involved in the provision of services.
Montreal Protocol
An MEA dealing the depletion of the earth’s ozone layer.
Most Favored Nation (MFN)
MFN (Article I of the GATT 1994) is the ‘normal’, non-discriminatory, tariff charged on imports between goods on the basis of their origin or destination. In commercial diplomacy, exporters seek MFN treatment that is, the promise that they get treated as well as the most favored exporter. Called Normal Trade Relations in the U.S.
MTN
See Multilateral Trade Negotiations.
Multifiber Arrangement (MFA)
“Arrangement Regarding International Trade in Textiles.” Negotiated as a temporary exception to the GATT in 1973. Regulates trade in certain textile products between signatories by means of negotiated bilateral quotas. Superceded by the WTO Agreement on Textiles and Clothing in 1995, which specifies that all quotas are to be abolished by 2005. They have been indeed eliminated on January 1st 2005.
Multilateral Trade Negotiations (MTN)
Trade negotiations between GATT (now WTO) Members aiming at eliminating or reducing tariff and non tariff barriers.
Multi-modal
Transportation using more than one mode. In the GATS negotiations, essentially door-to-door services that include international shipping.
N
National schedules
The equivalent of tariff schedules in GATT, laying down the commitments accepted – voluntarily or through negotiation – by WTO members.
National Tariff Line
National customs tariffs contain a list of all products which can be imported. Within the tariff, products are grouped according to the material they are made of, or according to the industrial sector to which they pertain either as input or as output materials (HS six-digit headings). Within those product groups customs tariffs contain as many tariff lines as there are different levels of customs duties. In other words, each duty rate is attached to a tariff line.
National Tariff Line Level
Most detailed level of tariff information for a given country. The list of tariff lines differs from one country to another one and standard nomenclatures (Harmonized System for example) are used to compare tariff structures among countries. See also National Tariff Line.
National Treatment
Obligation under Article III of the GATT 1994 which requires that imports be treated no less favourably than domestically-produced goods once they have passed customs.
Principle that foreign goods, services, and persons (investors), once they have entered a country and satisfied any formalities that are required, are treated in exactly the same way as national goods, services or persons. In particular, they face the same internal taxes and no additional restrictions.
Native Nomenclature
Nomenclature initially used by a country to report information. In WITS information may be converted in another available (derived) nomenclature.
Natural persons
People, as distinct from juridical persons such as companies and organizations.
Nature Of Duties
Nature of duties or the duty nature refer to the different kinds of customs duty. The duty nature can be an ad valorem, specific, compound, mixed, variable, “tariffied” or unclassified duty.
Negative list
In an international agreement, a list of those items, entities, products, etc. to which the agreement will not apply, the commitment being to apply the agreement to everything else. Contrasts with Positive List.
NGBT
Negotiating Group on Basic Telecommunications.
NGMTS
Negotiating Group on Maritime Transport Services.
Nomenclature
A nomenclature is an agreed system for classifying goods according to defined criteria, and in given detail and order, by associating to product groups a number which is used by all parties which adopt the nomenclature.
Nominal rate of protection
The proportion by which the (tariff-inclusive) internal price of an import exceeds the border or world price. See also Effective Rate of Protection.
Non-tariff barrier (NTB)
A catch-all phrase describing barriers to international trade other than the tariffs for example, quotas, licensing, voluntary export restraints.
Non-tariff measure
Any government action with a potential effect on the value, volume, or direction of trade. Also see Non-tariff Barrier.
Nullification and
Damage to a country’s benefits and expectations from its WTO membership impairment through another country’s change in its trade regime or failure to carry out its WTO obligations.
NTB
See Non Tariff Barrier.
NTL
See National Tariff Line
NTM
Non-tariff measures such as quotas, import licensing systems, sanitary regulations, prohibitions, etc.
See Non Tariff Measure.
O
Offer
A country’s proposal for further liberalization.
Origin Rule
See Rules of Origin
P
Panel
Consisting of three experts, this independent body is established by the DSB to examine and issue recommendations on a particular dispute in the light of WTO provisions.
Parallel imports
Trade that is made possible when a good that is protected under intellectual property provisions (patents, copyrights) is sold in different countries for different prices. A parallel import comprises arbitrage activity and occurs when traders import the good from a lower-price market into a higher-price country.
Para-Tariff
Charges on imports that act as a tariff but are not included in country’s tariff schedule. Examples include a statistical tax, stamp fees, etc.
Paris Convention
Treaty, administered by WIPO, for the protection of industrial intellectual property, i.e. patents, utility models, industrial designs, etc.
Partial Equilibrium Analysis
The study of one market in isolation, assuming that anything that happens in it does not materially affect any other market. SMART and GSIM are two Partial Equilibrium tools included in WITS.
Partner
Country of origin of imports or of destination of exports.
Peaks
See Tariff Peaks
Phytosanitary Regulation
Pertaining to the health of plants. See Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Measure.
Piracy Unauthorized copying of copyright materials for commercial purposes and unauthorized commercial dealing in copied materials.
Positive List
In an international agreement, a list of those items, entities, products, etc. to which the agreement will apply, with no commitment to apply the agreement to anything else.
PPM
Production and processing method. Used in instances where trade policy action by a country is motivated by a desire to ensure that imports have been produced in a way that satisfies a national or international production or process norm. Often these norms will be environmental in nature.
Precautionary principle
Policy under which measures are motivated by the possibility that use of certain technologies (e.g., biotechnology, genetically modified organisms, pesticides) could be harmful to human or animal health and safety or the environment, although there is no certainty to that effect.
Preference or Preferential treatment
In WTO terms, this represents derogation, in the sense of treatment that is more favorable than MFN. See also Generalized System of Preferences and Special and Differential Treatment.
Preshipment inspection
Mechanism under which goods are inspected and certified in the country of origin by specialized inspection agencies or firms. Often used by importing governments to combat over- or under-invoicing of imports by having the value of consignments determined by independent, foreign entities.
Price undertaking
Commitment by an exporter to either raise prices or reduce sales in a market as a way of settling an antidumping suit brought by import-competing domestic firms. Generally has an effect analogous to a quota.
Product Code
Standardized code identifying a product.
Product Aggregate
Group of products defined for analysis purpose (all textile products for example). WITS comes with a set of pre-defined aggregates and you can create your own.
Product-mandating
Requirement that the investor export to certain countries or region.
Protection data
All information related to market access and including notably tariff and non-tariff barrier information.
Protocols
Additional agreements attached to the GATS. The Second Protocol deals with the 1995 commitments on financial services. The Third Protocol deals with movement of natural persons.
Protocol of Accession
Legal document recording the conditions and obligations under which a country accedes to an international agreement or organization.
Prudence, prudential
In financial services, terms used to describe an objective of market regulation by authorities to protect investors and depositors, to avoid instability or crises.
PSI
Preshipment inspection – the practice of employing specialized private companies to check shipment details of goods ordered overseas – i.e. price, quantity, quality, etc.
Q
Quad
Canada, EC, Japan and the United States.
QR
Quantitative restrictions – specific limits on the quantity or value of goods that can be imported (or exported) during a specific time period.
Quad
Refers to the participants in the Quadrilateral meetings, i.e., Canada, the EU, Japan and the U.S.
Quantitative Restriction or Quota
Measure restricting the quantity of a good imported (or exported). Quantitative restrictions include quotas, non-automatic licensing, mixing regulations, voluntary export restraints, and prohibitions or embargoes.
▪ Global Quota
Quota specifying the total volume, or value, of the product to be imported (exported) without regard to the country or countries of origin (destination) of the product.
▪ Bilateral quota
Quota applied to imports from (exports to) a specific country.
▪ Quota by country
Quota which not only specifies the total volume, or value, of the product to be imported (exported), but also allocates the trade between the various countries of origin (destination).
QR
See Quantitative Restriction.
Quantitative Restrictions (QR)
Restriction which limits the value or quantity of goods which can be imported or exported during a given period.
Quantity Unit
The volume of imports is recorded in the statistical file. The unit used to express import volumes varies according to the product and according to the reporter. The quantity unit used is therefore attached to quantity data in the import statistics. The quantity unit is also used in the normalized code for specific duties.
Quota
See Quantitative Restriction
R
Re-Export
The export of imported goods without appreciable added value. Mostly used for goods which are transported through another country before reaching their final destination.
Reference Price
See Maximum/Minimum Price System.
Region
In WITS, refers to a group of countries used either to produce aggregated statistics or as a shortcut to select all countries belonging to that group.
Reporter
A country supplying data.
Reporting Country
See Reporter.
Request-Offer Procedure
Negotiating procedure based on the tabling, by each party, of a list of concessions requested of other parties, followed by an offer list of the concessions that could be granted if its request were met.
Retaliation
Imposition of a trade barrier in response to another country increasing its level of trade restrictions.
Revealed Comparative Advantage (RCA)
The ratio of a country’s exports of a good to the world’s exports of that good divided by that country’s share of exports of manufactures in the world exports of manufactures. The index for country i good j is RCAij = 100(Xij /Xwj)/(Xit /Xwt) where Xab is exports by country a (w=world) of good b (t=total for all goods). A value of the index above (below) one, is interpreted as a revealed comparative advantage (comparative disadvantage) for the good.
Rollback
The phasing out of measures inconsistent with the provisions of an agreement.
Rome Convention
Treaty, administered by WIPO, UNESCO and ILO, for the protection of the works of performers, broadcasting organizations and producers of phonograms.
Round
In WTO context, a multilateral trade negotiation. There have been 8 rounds
Geneva (1947), Annecy (1949), Torquay (1950-1), Geneva (1955-6), Dillon (1960-1), Kennedy (1963-7), Tokyo (1973-9) and Uruguay (1986-94). A ninth multilateral negotiation was launched in Doha, Qatar at the end of 2001.
Rules of Origin
Regulations to define a country of origin of goods in international trade. A country must satisfy the rules of origin to be considered as the country of origin of goods for the purpose of obtaining MFN treatment or preferential treatment.
S
Safeguard Action
Emergency protection to safeguard domestic producers of a specific good from an unforeseen surge in imports (GATT Art. XIX), to protect a country’s external financial position and balance-of-payments (GATT Art. XII, XVIII:B), or to protect an infant industry in a developing country (GATT Art. XVIII:A or C). See also Escape Clause.
Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Measure
A technical requirement specifying criteria to ensure food safety and animal and plant health. Many international SPS standards are set by the FAO/WHO.
Schedule
“Schedule of Specific Commitments” – A WTO member’s list of commitments regarding market access and bindings regarding national treatment.
Second-best argument (for protection)
Any argument for protection that can be countered by pointing to a less costly policy that would achieve the same desired result. Also refers to rationales for protection to partially correct a distortion in the economy when the first-best policy for that purpose is not available. For example, if domestic production generates a positive externality and a production subsidy to internalize it is not available, then a tariff may be second-best optimal.
Section
First level sub-category (1-digit) used in the SITC nomenclature.
Shallow integration
Reduction or elimination of border barriers to trade. Shallow integration contrasts with Deep Integration.
SITC
See Standard International Trade Classification.
SMART
Partial equilibrium model embedded in WITS which allows users to estimate the impact of tariff reductions on trade flows, tariff revenue, and consumer surplus for a single market at a time.
Specific commitments
Negotiated commitments on market access and national treatment by countries in their national schedules.
Special and differential treatment
The principle in WTO that developing countries be accorded special privileges, either exempting them from some WTO rules or granting them preferential treatment in the application of WTO rules.
Special Safeguard
In the WTO Agreement on Agriculture, a protectionist measure that can be triggered automatically by a decline in prices or an increase in imports.
Specific tariff
A specific duty is a customs duty which is not related to the value of the imported goods but to the weight, volume, surface, etc. of the goods. The specific duty stipulates how many units of currency are to be levied per unit of quantity (e.g. 2.00 Swiss Francs per KG).
SPS
See Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measure.
Stages Of Processing
For the analysis of the tariff escalation, products are classified according to their stage of processing. Products can be classified, in general, according to three stages of processing, namely, raw materials, semimanufactures and finished products.
Stages Of Reduction
Concessions offered in GATT negotiations are sometimes staged over a period of several years before the concession is fully implemented. For example, a duty reduction of 10 percentage points can be offered over 5 years with 5 equal stages of 2 points every year.
Standard
Rule, regulation or procedure specifying characteristics that must be met by a product (such as dimensions, quality, performance, or safety). When these put foreign producers at a disadvantage, they may constitute a non-tariff barrier. See also Technical Barrier to Trade.
Standard International Trade Classification (SITC)
The SITC is a classification developed by the United Nations for statistical analysis of trade data. In the SITC, articles are grouped by classes of goods such as food, raw materials, chemicals, machinery and transport equipment and also by stage of fabrication and by industrial origin. The SITC was first revised in 1960 (Revision 1) to match the Customs Cooperation Council nomenclature (CCCN). A second revision was established to match the revised version of the CCCN, in 1972. The third revision was established in 1985 to match the HS.
Statutory Duty
A customs duty which is generally a Customs Tariff Law voted by Parliament. The statutory duty is also referred to as the autonomous or legal duty. The published customs tariff generally report the statutory duty. For WTO Members, the statutory duty cannot be higher than the GATT bound duty.
Sub-Group
Fourth level sub-category (4-digit) used in the SITC nomenclature.
Sub-Heading
Third level and most detailed sub-category (6-digit) used in the Harmonized System (HS) nomenclature.
Subsidiary Heading
Fifth level and most detailed sub-category (5-digit) used in the SITC nomenclature.
Subsidy
Assistance granted by government to the production, manufacture or export of specific goods, and taking the form either of direct payments, such as grants or loans (also see Bounty), or of measures having equivalent effect, such as guarantees, operational or support services or facilities, and fiscal incentives.
Swing
When an exporting country transfer part of a quota from one product to another restrained product.
T
Tariff
See Customs Duty.
Tariff Base
Used within the WTO negotiations. Concept used within the tariff reduction process. The tariff base, once cut using a tariff reduction formula becomes the new Bound tariff structure.
Tariff Base Definition
Used within the WTO negotiations. It defines how to build the tariff base before applying the tariff reduction formula.
Tariff Binding
In GATT context, commitment by countries not to raise particular tariff items above a specific or bound level. Once a rate of duty is bound, it may not be raised without compensating the affected parties. Also referred to as ceiling bindings. The so-called schedule of tariff concessions of each WTO member is annexed to its Protocol of Accession. See also Ceiling Binding.
Tariff Equivalent
Measure of the protective effect of an NTB—the tariff that would have the exact same effect on imports as the NTB.
Tariff Escalation
Higher import duties on semi-processed products than on raw materials, and higher still on finished products. Occurs if the tariff increases as a good becomes more processed. Escalation discourages imports of more processed varieties of the good (discouraging foreign processing activity) and offers domestic processors positive levels of effective protection. This practice protects domestic processing industries and discourages the development of processing activity in the countries where raw materials originate. For example, low duties on tomatoes, higher duties on tomato paste, and yet higher duties on tomato ketchup.
Tariffication
Conversion of border measures, other than ordinary customs duties, to tariff equivalents of non-tariff measures. As part of the Uruguay Round Market Access for agricultural products, all non-tariff border measures were “tariffied” by participants before a tariff reduction was made.
Tariffied
See Tariffication
Tariff Peaks
Tariffs that are particularly high. Two measures of peaks are used:
▪ International Peaks: duties over 15%.
▪ National Peaks: duties over 3 times the average of the tariff structure.
Tariff rate quotas (TRQs)
Measure under which a good is subject to a MFN tariff, but a certain quantity (the ‘quota’) is admitted at a lower, sometimes zero, tariff. TRQs are mainly applied to agricultural trade and can be seasonal.
Technical Barrier to Trade
Trade restrictive effect arising from the application of technical regulations or standards such as testing requirements, labeling requirements, packaging requirements, marketing standards, certification requirements, origin marking requirements, health and safety regulations, and sanitary and phytosanitary regulations.
Technical Regulation
A mandatory requirement or standard specifying the characteristics that an imported product must meet. Usually aimed to protect public health or safety. See Technical Barrier to Trade.
Tier
Hierarchical level of organization within a given nomenclature. For example the Harmonized System (HS) nomenclature is composed of 3 tiers: Chapter (2-digit code), Heading (4-digit) and Sub-heading (6-digit). The more digits, the more categories and details.
TMB
The Textiles Monitoring Body, consisting of a chairman plus ten members acting in a personal capacity, oversees the implementation of ATC commitments.
TBT
Waiver Permission granted by WTO members allowing a WTO member not to comply with normal commitments. Waivers have time limits and extensions have to be justified.
Trade capacity
The supply-side ability (capacity) of a country to benefit from the opportunities offered by the world market and MFN or preferential access to markets.
Trade Control Measures
See Non Tariff Measures.
Trade-balancing
Requirement that the investor use earnings from exports to pay for imports.
Trade creation
Occurs when liberalization results in imports displacing less efficient local production and/or expanding consumption that was previously thwarted by artificially high prices due to protection.
Trade diversion
Occurs when a trade reform discriminates between different trading partners and a less efficient (higher cost) source displaces a more efficient (lower cost) one. Can arise whenever some preferred suppliers are freed from barriers but others are not.
Trade integration
Process of reducing barriers to trade and increasing participation in the international economy through trade. Also used to describe efforts to integrate trade policy and strengthening of trade-related institutions into a country’s overall development strategy.
TRAINS
See UNCTAD Trade Analysis and Information System.
Transitional
Allows members to impose restrictions against individual exporting countries safeguard if the importing country can show that both overall imports of a product and mechanism imports from the individual countries are entering the country in such increased quantities as to cause – or threaten – serious damage to the relevant domestic industry.
Transparency
Degree to which trade policies and practices, and the process by which they are established, are open and predictable.
Trigger Price
See Maximum/Minimum Price System.
TRIPS
Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights.
U
Unbound Duties
A customs duty rate is unbound if it was never subject to a tariff concession during any GATT round of tariff negotiations (see Tariff Binding).
UNCTAD
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
UNCTAD Trade Analysis and Information System (TRAINS)
HS-based tariff line level database covering tariff, para-tariff and non-tariff measures as well as import flows by origin for more than 140 countries.
UNSD
United Nations Statistics Division
UNSD Commodity Trade Statistics Database (COMTRADE)
Contains bilateral trade flows (import, export, re-export) information based on SITC and HS nomenclatures.
Upward Conversion
Consists of converting information from a given nomenclature to a newer one. Upward conversion is generally less accurate (than backward conversion) since the destination nomenclature is made of more lines and the conversion requires an expansion of the product structure.
V
Variable levy
Customs duty rate which varies in response to domestic price criterion.
Voluntary Export Restraint
Informal agreement between an exporter and an importer, whereby the former agrees to limit exports of a specified good to avoid dislocation of the industry in, and possible imposition of mandatory restrictions by, the importing country. The restraint agreement may be concluded at either industry or government level. In the latter case, sometimes referred to as an orderly marketing arrangement.
Voluntary Restraint Agreement
See Voluntary Export Restraint.
W
Waiver
Authorized deviation from a previously undertaken and legally binding obligation. Can be sought by WTO members through invocation of Art. IX WTO. Conditions under which waivers are granted are generally negotiated and limited in time.
Washington Treaty
Treaty for the protection of intellectual property in respect of lay-out designs of integrated circuits.
WIPO
World Intellectual Property Organization.
WITS
World Integrated Trade Solution—database and software package developed by UNCTAD and World Bank to allow analysis of market access conditions and the impact of own and partner country liberalization.
World
Country group used in WITS to aggregate all partner countries in one row of information.
WTO
World Trade Organization – established on 1 January 1995.
WTO Consolidated Tariff Schedules
The CTS database contains all WTO Members’ concessions (final bounds) on goods at the national tariff line level in a standardized format. The database was established as a working tool only, without implications as to the legal status of the information therein.
WTO Integrated Database (IDB)
The IDB contains annual tariff information (current MFN Bound and Applied tariffs) and import statistics on goods at the national tariff line level in a standardized format.
